2084 marks the beginning of a new era in healthcare, centered around a revolution in technological advancements. The rise of advanced body modifications, AI-driven diagnoses and drug delivery via drones illustrates the unprecedented possibilities that await the medical world. These developments promise a future in which the health and well-being of individuals is promoted and protected at an exceptional level.
Automated diagnoses and treatments
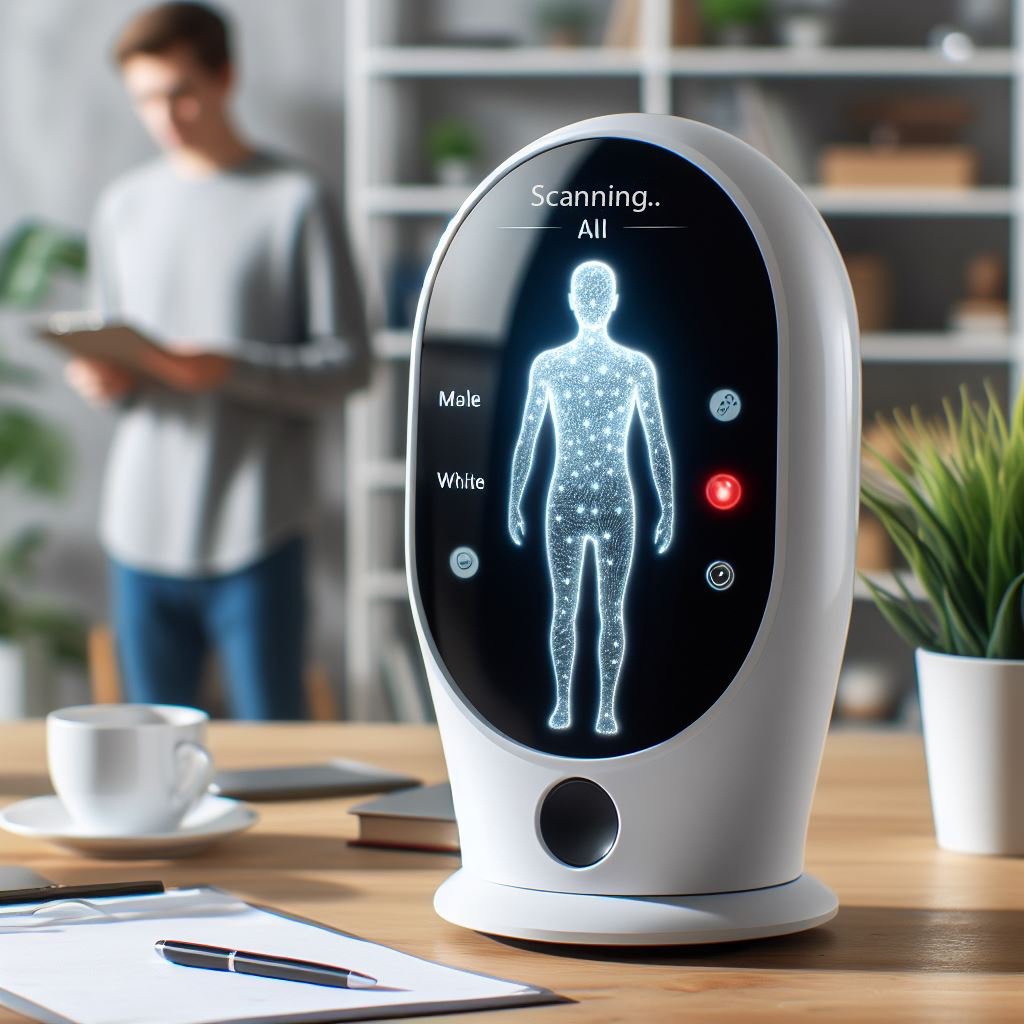

Using advanced AI algorithms, homepods in 2084 can perform a full body scan. By simply standing in front of the home pod, people can have their health checked without having to visit a doctor. The homepod analyzes vital functions, scans for possible abnormalities and makes accurate diagnoses based on collected data. But it doesn't stop at diagnosis alone. These home pods are also connected to an automated medicine supply system. After making a diagnosis, users can order the necessary medication with a simple voice command. And this is where the magic really begins.
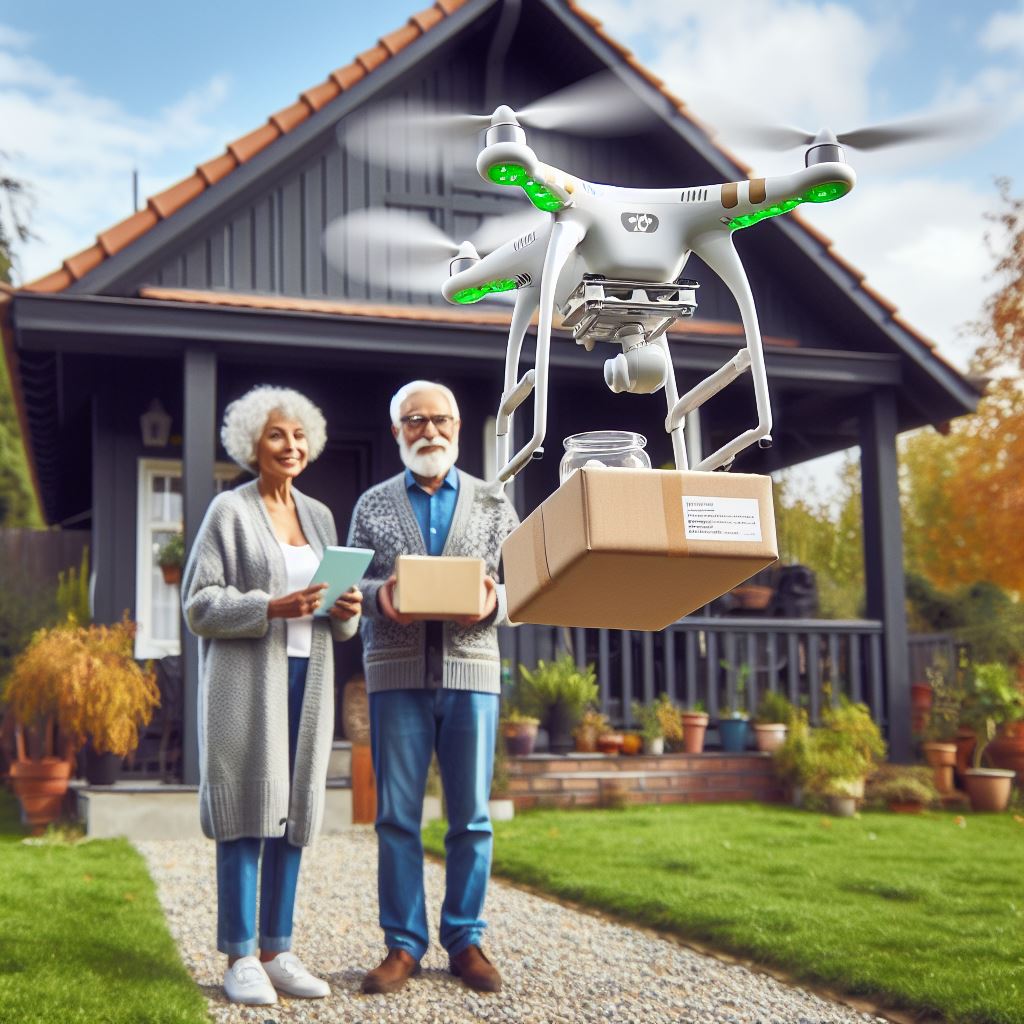
Once ordered, the medication is delivered not by traditional couriers, but by drones. These drones deftly navigate the air and deliver the medicines directly to the patient's door. This efficient and fast delivery system ensures that people no longer have to wait for important medication, significantly improving the health and well-being of Ghent residents.
In short, in 2084, home pods are not only entertainment and information systems, but also medical companions that can diagnose and provide access to essential medications, all from the convenience of being at home.

Body mods and technological advancements
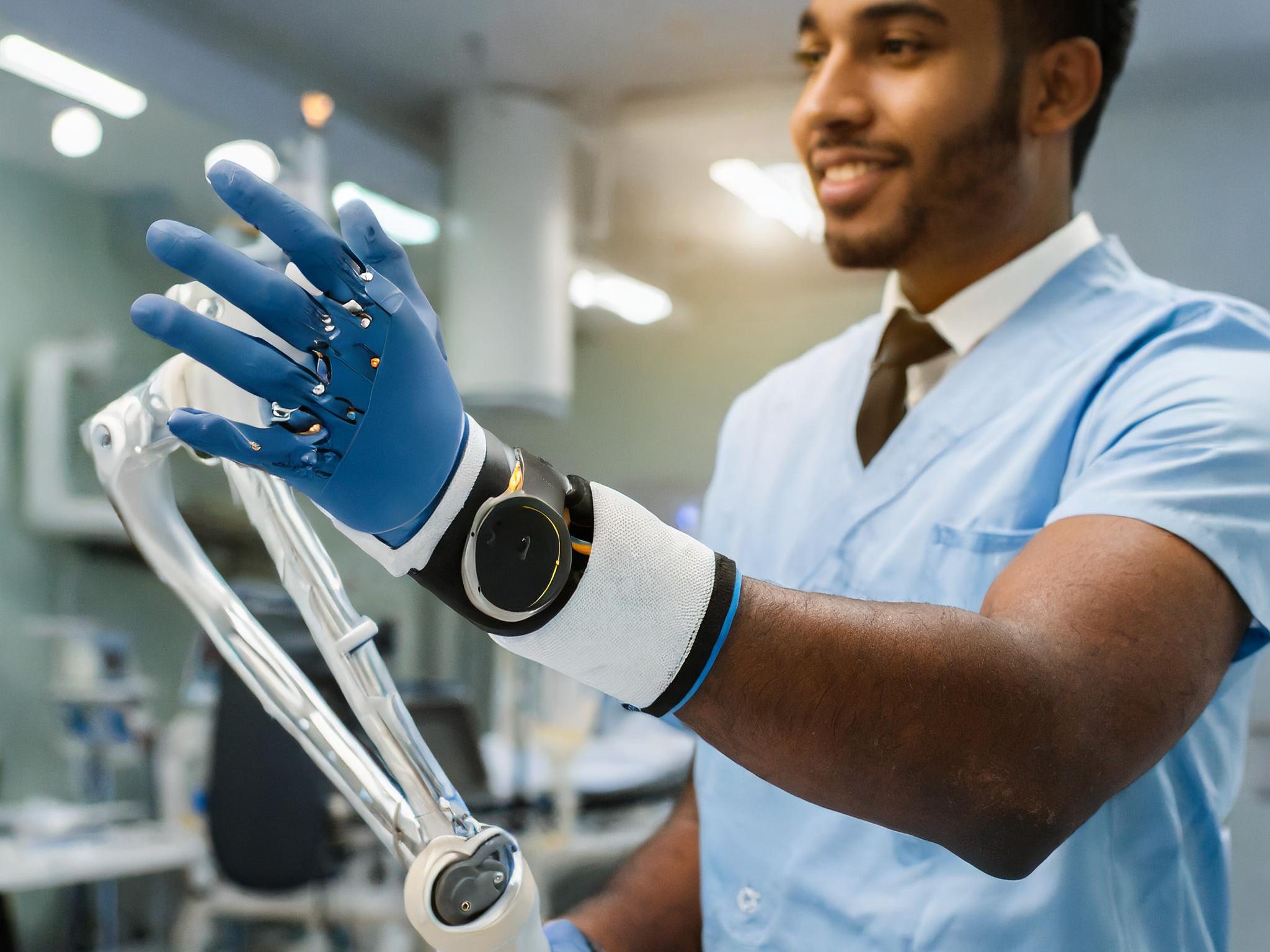

Body modifications occupy an essential place. Think of advanced surgical implants that stabilize hand movements. These technological advances promise not only a more efficient work process, but also a reduction in complications in complex matters. These innovations not only expand the possibilities of modern medicine, but also improve the quality of life for many.
Meaningful interactions in a digitalized world
In a world that is becoming increasingly digitalized, human contact remains an indispensable element in healthcare. Although technology plays a greater role in diagnosis, treatment and care delivery, this vision strives for a balance between technological progress and human involvement. It is essential that both patients and caregivers feel connected, resulting in a healthcare environment that focuses on empathy, understanding and support. This integration of technology with human interaction promises healthcare that is not only efficient and advanced, but also warm and human.

The social and ethical aspects
With the remarkable advancements in healthcare powered by artificial intelligence, we have reached a new horizon of possibilities. People now enjoy significantly longer life expectancies and can recover from illness and injury faster than ever before. However, these technological triumphs have also raised an ethical question that forces us to reflect deeply: where is the limit of human lifespan?
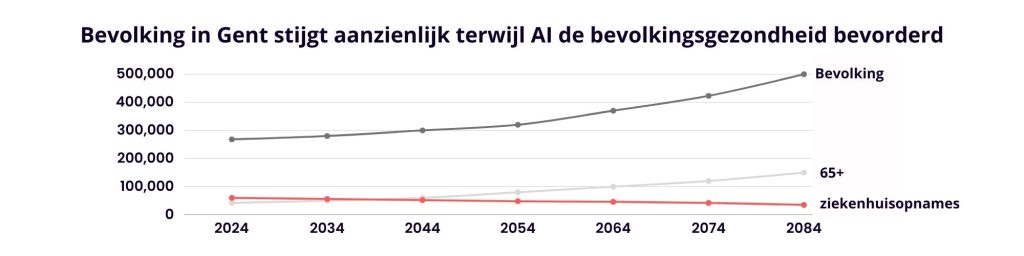
With the rise of AI in healthcare, coupled with the extension of lifespan and improved chances of recovery, we are faced with a dilemma that is not only ethical in nature, but also has practical implications for the residents of Ghent. One of the consequences of longer life expectancy is the increasing aging of the population and the associated challenges, such as increased pressure on social services and pension systems.
While we cheer for the opportunity to fight disease and give people longer, healthier lives, we must be aware of its broader impact. An aging population can lead to labor shortages and pressure on the economy as a whole.
Furthermore, lifespan extension can also lead to overpopulation and further burden on natural resources and infrastructure. This brings new challenges in the areas of urban planning, environmental pollution and food supply.
Fortunately, by then, Ghent has invested well in a healthcare system in which care is virtually free for all citizens.
This means that despite the ethical and practical challenges of an aging population and possible overpopulation, people can count on quality medical care without having to worry about financial barriers. A universal healthcare system provides a safety net for individuals and families who might not otherwise have access to life-saving treatments and medications.
By maintaining a healthcare system in which care is almost free for everyone, the city of Ghent can reduce health disparities and build a more just society. This contributes to the general health and well-being of the population and reduces social inequality that is often associated with inadequate access to care.
So as we consider the ethical and practical implications of longer life and improved chances of recovery, we can take comfort in the fact that in some parts of the world there is a healthcare system in which care is virtually free for all, thus safeguarding the right to health.